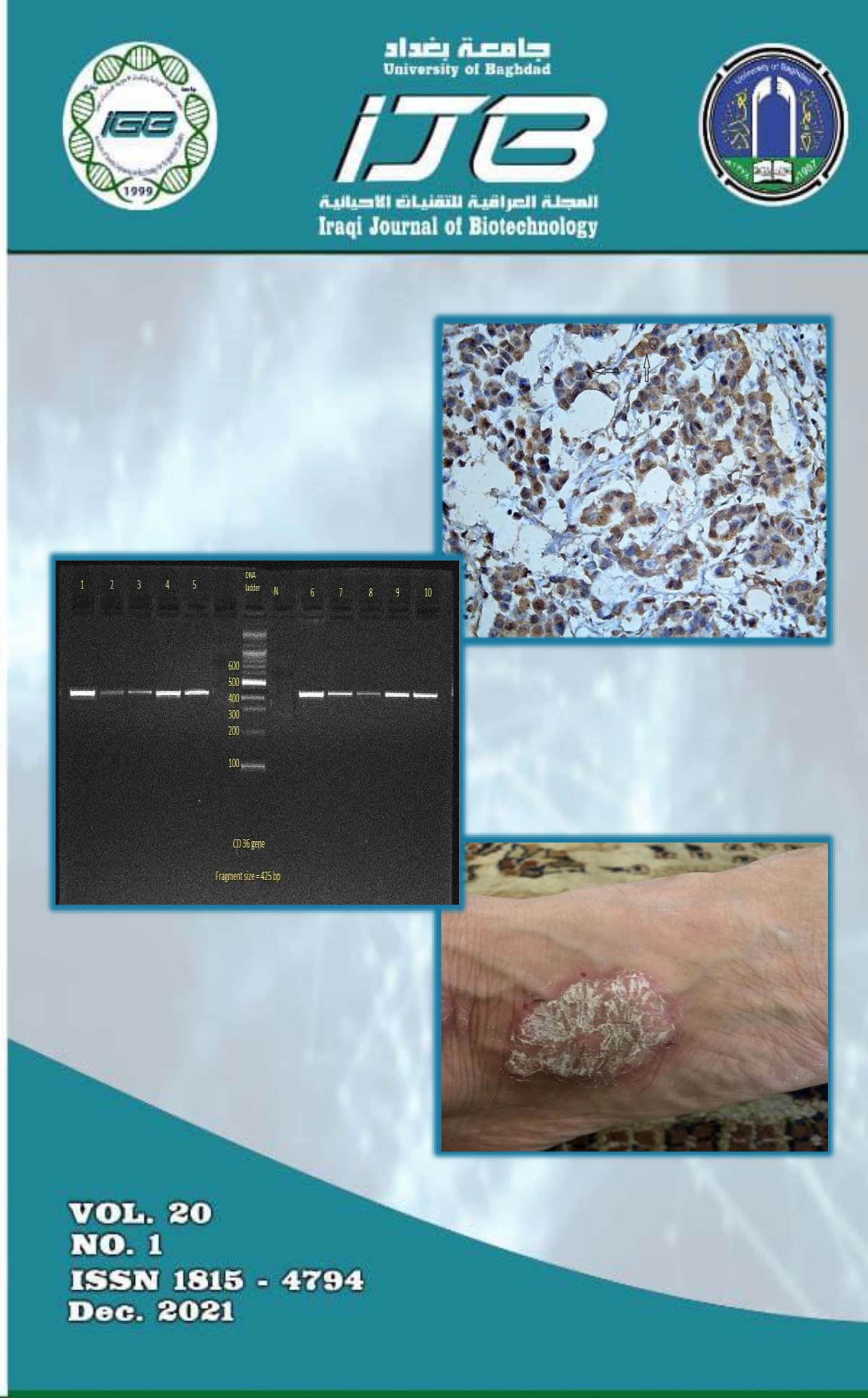
Detection of Epstein Barr Virus in Some Iraqi Women Patients with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Using Immunohistochemistry Technique
Abstract
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is a common breast cancer especially in women. Several factors may involve in establishment of the breast cancer in general. Variant viruses have been investigated in for their role in the establishment of breast cancer, among them is Epstein Barr virus which has been reported in the patients diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma. The study aimed to detect the presence of Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) in a group of Iraqi women diagnosed with IDC and to correlate expression patterns with the age of the participants and with the grade and stage of cancer. A total of 30 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue of IDC biopsy samples and 29 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues of fibroadenoma as controls were collected to detect the presence of EBV LMP1 using immunohistochemistry. LMP1 expression was found in 76.67% of cases and in 58.62% of the control specimens. The expression pattern of LMP1 was determined to be statistically significant (P=0.0037) when correlated with age, grade and stage. As well as immunohistochemistry was found to be a sensitive technique in the detection of EBV. Conclusions: The study reveals that the LMP1 was over expressed in our population